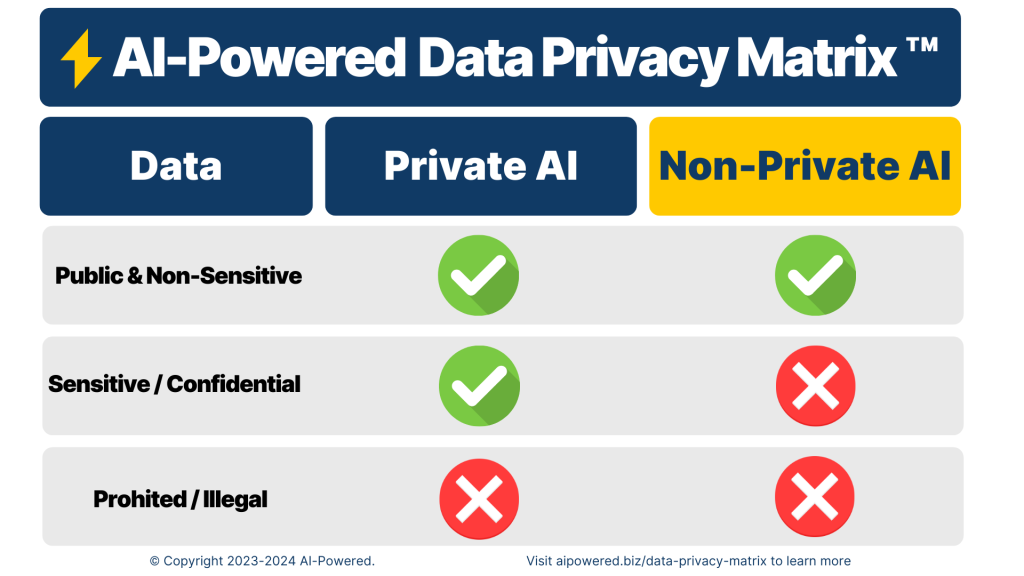
The AI-Powered Data Privacy Matrix™ helps you understand what data is safe to input into AI systems. It categorises AI systems based on their privacy features and sorts data types by sensitivity. This is important for making better decisions while staying compliant with legal and ethical standards.
As AI tools become more common in business, protecting sensitive data is critical. The matrix gives you a simple, clear path to follow, so you can manage your data with confidence.
Why This Matters
When you use AI tools—like chatbots or virtual assistants—you’re sharing different types of data. Some of this data could be personal, private, or legally protected. If you don’t understand the risks, you could face data breaches, legal issues, and a loss of trust.
The AI-Powered Data Privacy Matrix™ helps you:
- Keep private data secure by avoiding sharing it inappropriately.
- Ensure compliance with laws like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Make better decisions when using AI, while staying ethical.
Understanding AI Systems and Data Types
Types of AI Systems:
The matrix divides AI systems into two main categories:
- Private AI: These systems don’t use your data for training, meaning your data isn’t read or stored for future use. Your input remains private and isn’t shared. Examples include:
- Self-hosted AI that runs on your hardware.
- Paid AI services with strong privacy and clear data handling policies.
- Non-Private AI: These systems may use your data for training or store it for future processing. Examples include:
- Free AI services.
- Online AI services with unclear privacy policies.
Private AI Isn’t Always the Same:
Even within Private AI, there are differences:
- Trusted Providers: Some AI providers offer good privacy protections and let you opt out of data being used for training. Look for:
- The provider’s reputation.
- The clarity of their privacy policies.
- Regulatory compliance.
- Their security measures.
- Self-Hosted vs. Cloud-Based: Self-hosted AI gives you full control as your data stays on your system. Cloud-based services, even private ones, still move data over the internet.
Types of Data:
Understanding Data Categories
We’ve simplified data into three categories:
1. Sensitive and Confidential Data
- Definition: Information protected by privacy laws, confidentiality agreements, or competitive reasons.
- Examples:
- Personal Data: Names, addresses, phone numbers, medical records, financial information.
- Third-Party Personal Data: Information about other people, like employees or customers.
- Company Confidential Information: Business strategies, trade secrets, internal reports.
- Intellectual Property (IP): Proprietary code, patents, copyrighted material.
- Regulated Data: Data protected by laws, such as health records or information about minors.
2. Public and Non-Sensitive Data
- Definition: Publicly available information, non-sensitive data, or data you’re comfortable sharing.
- Examples:
- Public Domain Information: Published research, public statistics, widely known facts.
- General Knowledge Queries: Common questions or information requests.
- User-Generated Content: Your own writings or content you’re happy to share.
- Anonymised Data: Data with personal identifiers removed.
3. Prohibited or Illegal Content
- Definition: Content that is offensive, illegal, or violates terms of service.
- Examples:
- Offensive Content: Hate speech, discriminatory remarks.
- Illegal Content: Content that violates laws or regulations.
Using the AI-Powered Data Privacy Matrix™
Here’s how to use the matrix to decide if it’s safe to share data with AI:
- Identify the AI System: Determine if the AI is a Private AI or Non-Private AI.
- Check your organisation’s AI policy for approved systems.
- Review the AI provider’s privacy policy.
- Check if the AI uses data for training. For example, when logged into AI-Powered ChatGPT, it shows that data isn’t used for training models.
- Classify Your Data: Identify which data type you’re dealing with.
- Consult the Matrix: Use the matrix to decide if it’s safe to share that data.
Example:
You want to use a free AI chatbot to analyse a confidential business proposal. Here’s how the matrix applies:
- AI System: Non-Private AI (a free chatbot with unclear privacy policies).
- Data Type: Confidential business information.
Matrix Guidance: The matrix advises against sharing confidential data with non-private AI due to risks of data misuse or unauthorised access.
The AI-Powered Data Privacy Matrix™
Other Factors to Consider
The matrix is helpful, but there are other things to keep in mind:
- Security: Ensure strong security measures in AI systems, especially private ones.
- Data Retention: Understand how long your data is stored.
- Share Less Data: Only share what’s necessary.
- Consent and Compliance: Get permission for third-party data and follow the law.
- Data Anonymisation: Remove personal details before sharing data with AI.
- Review the Terms: Regularly check the AI provider’s terms of service for changes.
- Ethical Considerations: Consider the ethical implications of sharing certain data.
- Reassess Regularly: Keep evaluating the trustworthiness of the AI system.
Conclusion
The AI-Powered Data Privacy Matrix™ helps you make informed decisions about sharing data with AI systems. By understanding the type of AI you’re using and the data involved, you can stay secure, compliant, and ethical in your AI use.